Operators in C#
We will explore the different operators in C# and perform some operations.
Arithmetic Operators
Below are the arithmetic operators being supported in C#:

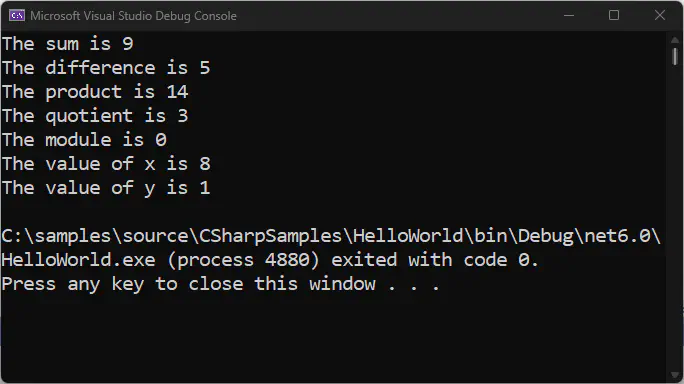
Here’s a sample program on how they are being used in C#:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int sum = 0, difference = 0, product = 0, modulo = 0;
double quotient = 0;
int x = 7, y = 2;
sum = x + y;
difference = x - y;
product = x * y;
quotient = x / y;
modulo = 6 % y;
Console.WriteLine("The sum is " + sum);
Console.WriteLine("The difference is " + difference);
Console.WriteLine("The product is " + product);
Console.WriteLine("The quotient is " + quotient);
Console.WriteLine("The module is " + modulo);
x++;
y--;
Console.WriteLine("The value of x is " + x);
Console.WriteLine("The value of y is " + y);
}
}
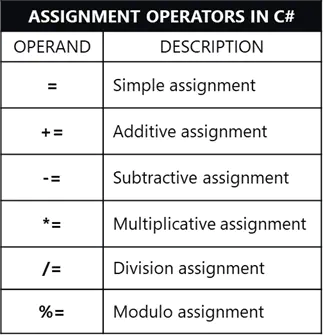
Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables.
Below are the common assignment operators used in C#:
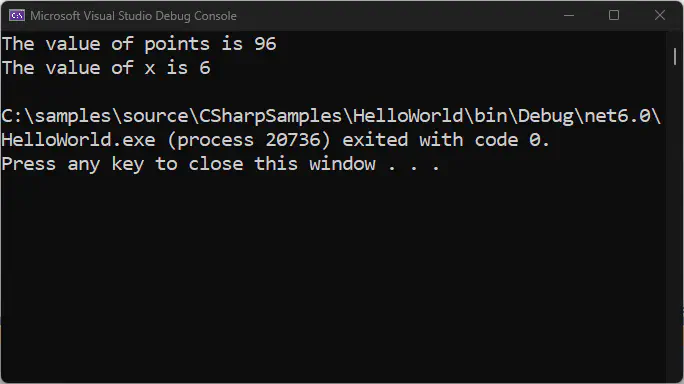
Here’s a sample program on how they are being used in C#:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int points = 96; //assigning value to a variable
Console.WriteLine("The value of points is " + points);
int x = 1;
x += 5;
Console.WriteLine("The value of x is " + x);
}
}
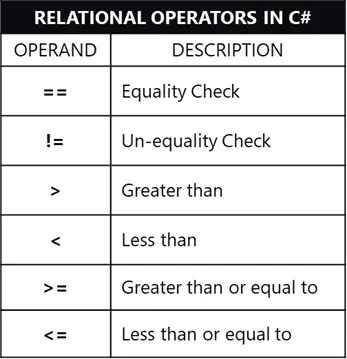
Relational Operators
Relational operators are used for comparison purposes in conditional statements. Relational operators always result in a boolean statement (either true or false) but only compatible data types can be compared.
Below are the common relational operators in C#:
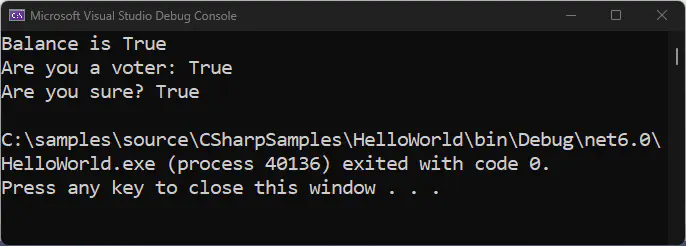
Here’s a sample program on how they are being used in C#:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool balance = 2 == 2;
Console.WriteLine("Balance is " + balance);
bool voter = 8 < 18;
Console.WriteLine("Are you a voter: " + voter);
int sure = 1;
Console.WriteLine("Are you sure? " + (sure != 0));
}
}
Logical Operators
Logical operators are used for logical calculations.
Below are the common logical operators being supported by C#:
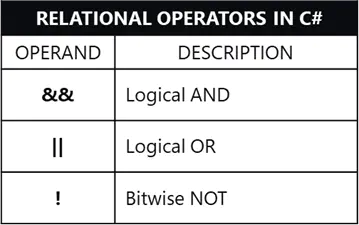
The NOT operator is used to negate a boolean expression. && and || are used to combine comparisons.
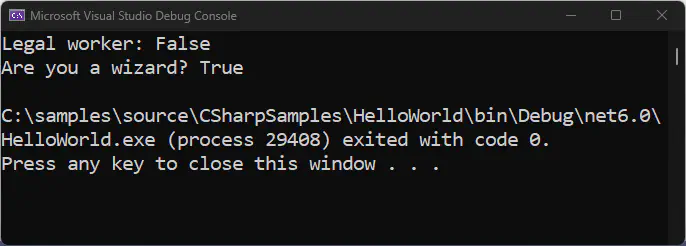
Also down below is sample code on how these logical operators are being used in C#:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int age = 12;
Console.WriteLine("Legal worker: " + (age < 18 && age >= 65));
string father = "Wizard";
string mother = "Muggle";
bool wizard = father == "Wizard" || mother == "Wizard";
Console.WriteLine("Are you a wizard? " + wizard);
}
}
Other Operators and Operator Precedence
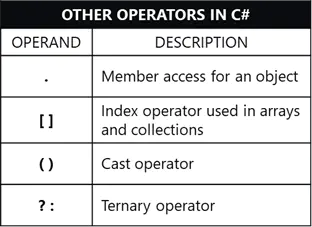
Aside from already mentioned operators above, there are also other important operators in C#.
Below are the most common of them:
Just like in Mathematics, not all operators are created equal. A concept of “operator precedence” is also being applied in C#.
Consider the following example:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 10, b = 5, c = 2;
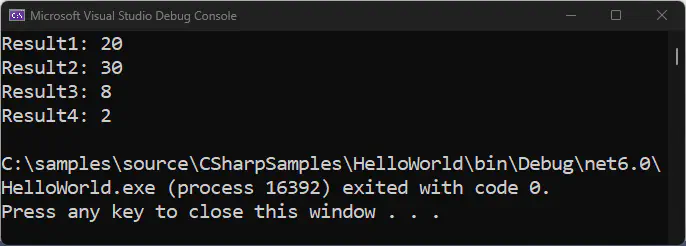
int result1 = a + b * c; // result1 = 20
int result2 = (a + b) * c; // result2 = 30
int result3 = a - b / c; // result3 = 8
int result4 = (a - b) / c; // result4 = 2
Console.WriteLine("Result1: " + result1);
Console.WriteLine("Result2: " + result2);
Console.WriteLine("Result3: " + result3);
Console.WriteLine("Result4: " + result4);
}
}
🔚 end of document 🔚